Lexus recently revealed the LF-ZC concept at the ongoing Japan Mobility Show 2023. The LF-ZC is the next-generation battery electric vehicle (BEV) from Lexus that’s slated to go on sale in 2026.
Lexus LF-ZC, which stands for Lexus Future Zero-Emission Catalyst, showcases the next-generation BEV platform from the Japanese carmaker. Boasting the sedan body style, Lexus claims the LF-ZC carries new-gen components taking considerably less space thus maximising seating space and comfort.

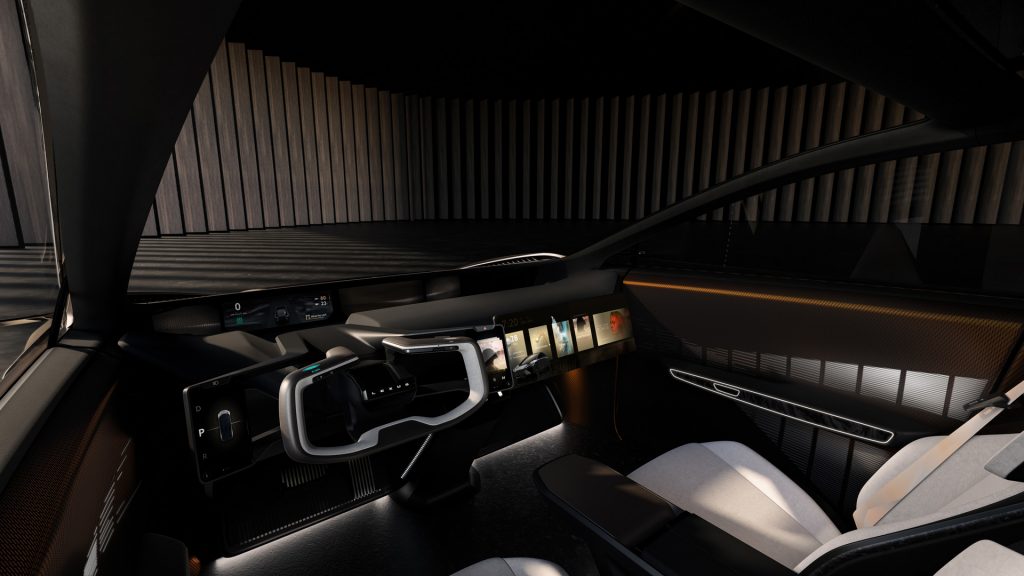
The Lexus LF-ZC will offer an all-wheel-drive DIRECT4 system and a steer-by-wire system offering a natural and linear steering wheel. On the inside, the Lexus LF-ZC concept features Bamboo CMF material which is sustainable. Other highlights of the LF-ZC concept include digital controls for shifting, ADAS and drive mode selection.


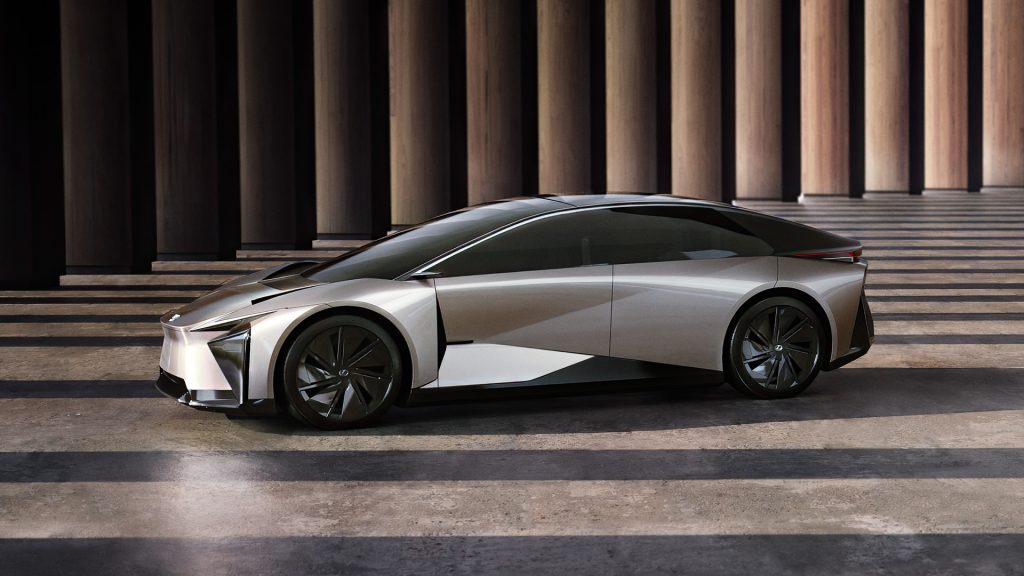
On the design front, the Lexus LF-ZC concept features the new design philosophy from Lexus that is very aerodynamic, claiming a drag coefficient of 0.2d. Its low-slung hood and tapering roofline give it a dynamic stance, which is further accentuated with various cuts and creases flowing around the side.
The production-spec Lexus LF-ZC will feature next-generation prismatic high-performance batteries, which claim to offer double the range of conventional EVs. Since the batteries are placed between the wheels, the centre of gravity is low and the floor is also flat, maximising space on the inside. In terms of dimensions, the LF-ZC measures 4750mm in length, 1880mm in width, 1390mm in height and sports a wheelbase of 2890mm.
Continuing with the idea of subscription-based services, the LF-ZC will feature the Arene OS. With this system, the owners will have the option to tweak the performance settings on the go based on the situation. The next-generation voice recognition of the LF-ZC will also use advanced AI technology to mimic the one-on-one interaction with an attentive butler.
The next-gen Lexus BEVs, including the LF-ZC, will feature a new modular structure formed through gigacasting, which splits the vehicle body into three parts: front, centre, and rear. Additionally, the new production process will also introduce a self-driving assembly line, where vehicles fitted with batteries, motors and tyres will drive to the next assembly state itself.

